The world has seen a dramatic change since the last All Things AI webinar in February. We’re now in the midst of a global pandemic and all eyes are on one sector in particular: the healthcare sector. It’s with that in mind that we turned our attention to Artificial Intelligence (AI) in healthcare for the latest webinar in the series. You can watch the full webinar on-demand now.
Joining our webinar host Craig McCartney and series chair David Skerrett was a very special guest. Michael O’Connell is the Chief Analytics Officer at TIBCO Software, and he brought a range of exceptional use cases and discussion points for the state of AI in healthcare.
Didn’t get to see the webinar or in need of a recap? Here’s our brief summary of what went down during the live webinar with TIBCO Software and details on how to download the on-demand webinar.


AI in Healthcare Today
David Skerrett, Drum Digerati and digital transformation expert, kicked off our webinar and got our audience up to speed on the state of AI in the healthcare sector today.
Firstly, David took a look at the history of hospitals. His research suggests that hospitals have been around since the 9th century, and have gone through four revolutions. But it wasn’t until the introduction of sanitation in the 19th century that the quality of healthcare dramatically improved and life expectancy started increasing. The 20th century saw a further boom in life expectancy with the invention of antibiotics and vaccines.
Now, we’re seeing a new revolution in healthcare, one powered by digital technology and, in particular, analytics and AI. On the one hand, life expectancy will continue to see improvements. But some of the most impressive statistics come in where cost efficiencies are concerned. For instance, David shared that AI applications can create $150 billion in annual savings for the United States’ healthcare economy by 2026. Meanwhile, the top three applications that represent the greatest near-term value are robot-assisted surgery ($40 billion), virtual nursing assistants ($20 billion) and administrative workflow assistance ($18 billion). With savings and new value creation like this, healthcare organisations will be able to redeploy efforts and treat patients more efficiently.
There are other areas that David highlighted as a possible beneficiary of AI/ML: chronic health conditions. Research suggests that AI/ML will help to develop new treatments for cancer (63%), heart disease (63%) and diabetes (66%). But we don’t have to wait for new AI solutions to see the benefits the technology is already having on the healthcare sector. David discussed how Diagnosis, Treatment, Drug Design, Predictions & Efficiency, and Patient Care are all benefitting from AI solutions today.
- Diagnosis: Misdiagnosing illness and medical error accounted for 10% of all US deaths in 2015. AI tools can rapidly identify patterns in big data to diagnose accurately.
- Treatment: AI can personalise treatments to the patient, providing unparalleled insights into how a drug is performing in real-time. If a better treatment plan is available, the solution will recommend it.
- Drug Design: With getting new drugs to human trial extremely expensive and time consuming, AI solutions are helping to identify the most suitable drug choices and save time and money.
- Predictions & Efficiency: Predictive analytics is helping healthcare managers to optimise business operations and patient care through optimising staffing levels, increasing utilisation, and predicting demand.
- Patient Care: AI-powered chatbots are helping to take the strain off call centres by answering patient questions autonomously. Some organisations have even deployed chatbots to help in the coronavirus pandemic.


Drug Design, Predictions & Efficiencies
with Michael O’Connell
After David had finished setting the scene, we moved to Michael’s section of the webinar, an in-depth look at a handful of major use cases for AI in healthcare. Drawing on his experience working with US healthcare providers as part of his role as Chief Analytics Officer at TIBCO Software, Michael first discussed drug design before looking at predictions and efficiency improvements.
To start our tour of TIBCO’s AI use cases in healthcare, Michael looked at translational medicine and high content screening. For a detailed look into what Michael unveiled, view the full webinar now.

In Michael’s translational medicine example, he highlighted how AI and ML solutions accurately predict clinical outcomes for potential drugs. These solutions are sequencing molecular states and identifying the small number of clinically significant molecular states from millions of features. It works by identifying common biomarkers between new molecules and existing drugs which have vast amounts of data to work with. Established patterns and relationships reveal the potential survival rates, risk scores and novel treatment plans of new drugs.
Michael then turned his attention to high content screening, where automated microscopes capture millions of images of cells in a variety of conditions to analyse drug effectiveness. As he showed, the data analysis workflow of today can sometimes be very convoluted. It must go through six stages: Automated Image Capture; Image Pre-Processing; Segmentation; Feature Extraction; Feature Reduction & Aggregation; Visualisation & Interpretation. TIBCO’s Spotfire solution streamlines this approach. Its deep learning algorithm has been trained on whole images, not individual objects, so segmentation isn’t needed, bringing AI automation to screening and addressing bottlenecks.


How TIBCO Helped Optimise Surgical Workflow
But perhaps Michael’s most exciting example of AI use within the healthcare sector came when looking at Operation Room (OR) efficiencies. You may not know this, but the OR is the most expensive minute in a hospital. Every minute that an OR stands idle, it costs the hospital $625 on average. That’s money that could be better spent actively saving lives by improving the efficiency of the hospital and its OR.
TIBCO’s Spotfire analytics solution enables the optimisation of surgery operations including on-time starts, scheduling accuracy, and block utilisation. When used by Saint Francis Hospital and Medical Center, measurable results included a 25% improvement in first case on-time starts, a 20% increase in surgery block utilisation and an estimated $450,000 value of surgery time created. Ultimately, the solution has led to better time allocation and more patients being treated, all while generating cost savings.
Elsewhere, TIBCO’s software has also helped to identify which patients will suffer post-surgery infections. By predicting which patients are most at risk, the software has allowed healthcare professionals to take a proactive approach to infection, shielding vulnerable patients and reducing the likelihood of hospital readmissions due to on-site infection – which cost US hospitals $45 billion annually.
To truly understand how TIBCO has brought about real positive change to the healthcare sector with its AI solutions, download the full webinar for free now.


The Good, the Bad and the Ugly… Or Just Good?
Regular viewers of this series will know that at this stage of the webinar we normally open the floor up to our audience. This is where we ask you to vote on a selection of AI use cases and judge them as Good, Bad or Ugly. But in the latest webinar, we decided to skip the vote – all of the AI use cases were obviously good! Here they are in full:
AI & Empathy Take on Covid-19
In early April 2020, Stanford professor and HAI co-director Dr Fei-Fei Li presented a concept for an AI-powered in-home system that could track a resident’s health, including signs of Covid-19 – all while meeting privacy standards. The system would use cameras and depth, thermal, and wearable sensors to monitor the user’s health.

AI for Employee Back-to-Work Scheme in Covid-19 World
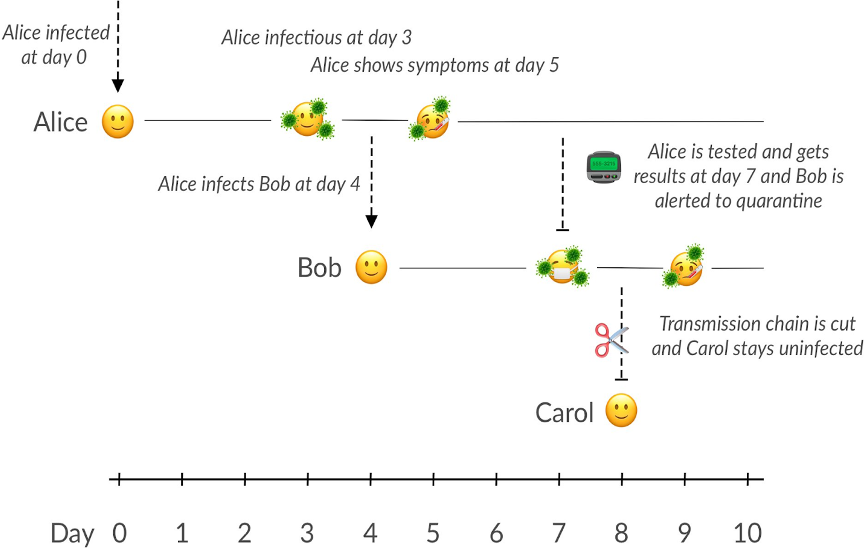
There are a number of AI-driven digital systems emerging to test, trace and isolate people infected by SARS-CoV-2.
Apple and Google announced a joint initiative that allows phones to broadcast crypto-generated codes via Bluetooth. The codes don’t include private data, but do tie the codes to one person. As a person moves around, other phones would recognise the crypto-tag and record the movement. If a person then gets infected with Covid-19, the people they had come into contact with would be notified and they could go and get tested.
The Trace Together app in Singapore also uses Bluetooth to regonise nearby phones and exchange anonymised and encrypted IDs. It works in a similar way to the above example. Approximately 20% of the Singapore population have downloaded the app.

AI Reads Minds to Give the Silent a Voice
Reading minds might sound like science fiction, but we’re a lot closer than you might think. Scientists have now developed an AI solution that can turn brain activity into text. Researchers Makin, Moses and Chang in San Francisco have been looking at neural patterns while someone is speaking aloud and are training algorithms to identify words when neural activity related to speech is triggered. Accuracy with implanted brain electrodes has been 95%, and could help people who can’t talk or type to communicate.

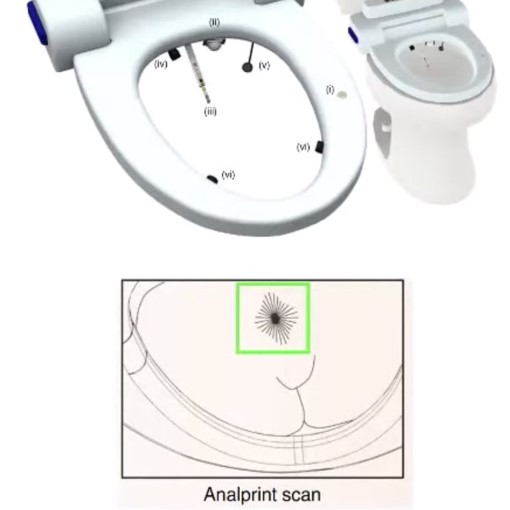
AI Smart Toilet Monitors for Signs of Disease
The Internet of Things is ever expanding, but did you think it would move into toilets so quickly? This AI solution uses technology that can detect a range of disease markers in stool and urine samples, including those of some cancers such as colorectal or urologic cancers. It uses cameras, motion sensing, deep learning CNNs and physical and molecular analysis to assess disease characteristics. It then automatically uploads data to a cloud-based system and integrated into a health care provider’s system for assessment.
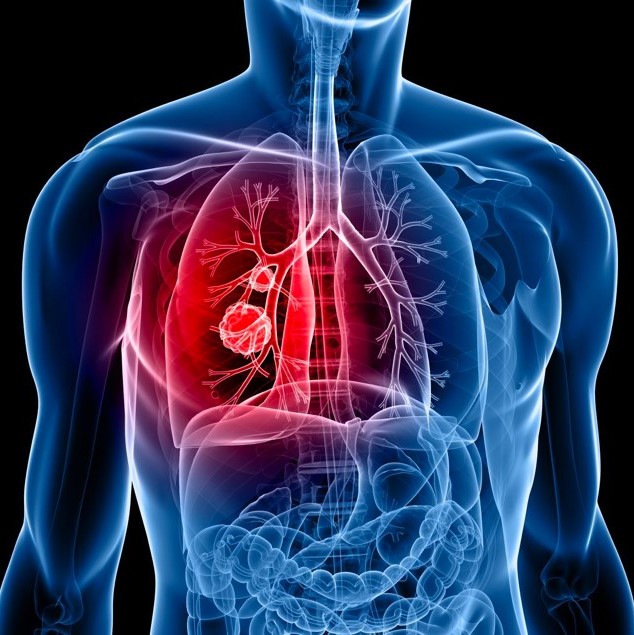
AI in Early Detection of Lung Cancer
In 2020, scientists Chabon and Hamilton developed an AI program that can screen people for lung cancer by analysing their blood for DNA mutations that fuel the disease. The software is yet to be trialled, but if it’s accurate and scales, it will boost lung cancer screening rates by simplifying the process. Oncologists diagnose 60-70% of lung cancers during Stage 4 – this AI solution should help detect them earlier and make recovery and remission more likely.

AI Detection of Surgical Site Infection
Surgical site infection (SSI) is the number one cause of readmission in surgical patients. By combining data from the electronic medical record, hospital operations and real-time data from the OR, this AI/ML model application predicts the risk of SSI in patients before, during and after surgery. The cost of intervention to prevent SSI is just $500, but the cost of readmission due to SSI is $28,000. So even if the solution generates 56 false positives, if it still produces 1 false negative it has still created significant value.
Meet Our Sponsors, TIBCO Software

TIBCO Software proudly sponsored the sixth instalment of the All Things AI webinar series. TIBCO is a leading independent provider of infrastructure software, including integration, analytics and event-processing software. Over 10,000 customers manage their information, decisions, processes and applications through TIBCO. To find out why they trust TIBCO’s software, head to their website now and lay the foundation for your digital innovation with the TIBCO Connected Intelligence Cloud.